
Get the Booklet
Download the Brain and Brain Injury Publication in pdf format
The Lobes of the Brain – Interactive!
Try our short learning module below to interact with the various Lobes of the Brain and find out more about what they do.
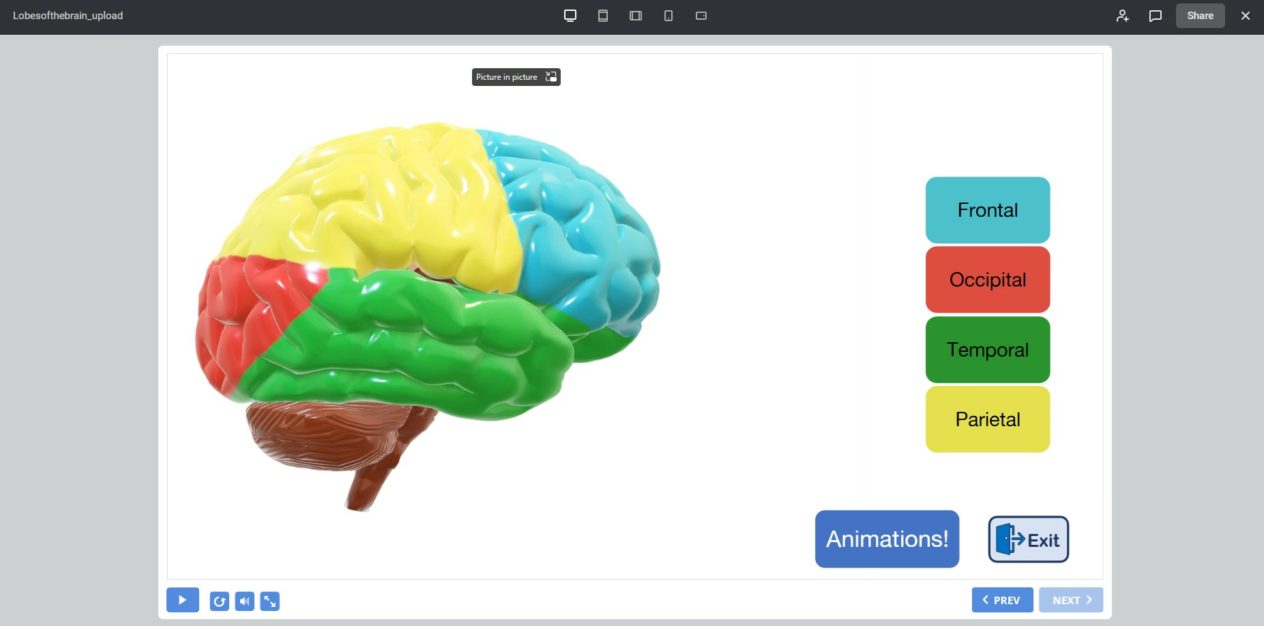
View it at this link
Introduction
Each half of the brain is divided into four areas called Lobes.
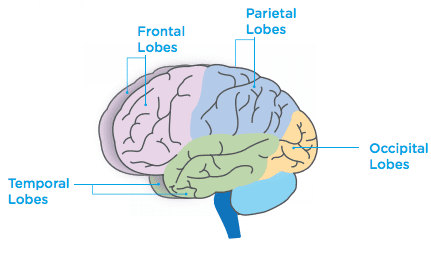
The Frontal Lobes
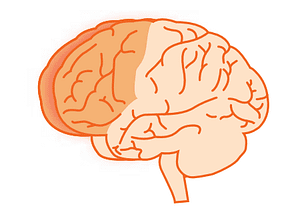
The frontal lobes manage skills known as Executive Functions. These are very important skills we use for things such as solving problems, planning, making decisions and controlling our behaviour. The frontal lobes work like the conductor of an orchestra who keeps all the musicians playing together harmoniously.
Some Effects of an Injury to the Frontal Lobes
The frontal lobes are particularly vulnerable to injury because they are large and are at the front of the brain. An injury to the frontal lobes can lead to a number of changes including:

- Changes in personality.
- Difficulties with attention and taking in information.
- Emotional responses may be reduced.
- Difficulties with motivation (Apathy) or getting things started (Initiation).
- Changes in the ability to control behaviour (Disinhibition). This means that the person may be more impulsive. They may say or do things without considering the consequences.
- Reduced self-awareness (Anosagnosia).
- Poor judgment and decision-making.
- Difficulty planning things and meeting goals.
- ‘Black and white’ thinking (Concrete Thinking).
- Irritability and less tolerance of frustration.
The Temporal Lobes
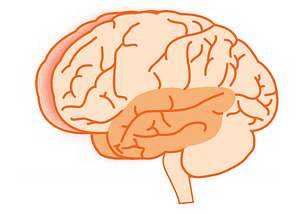
Some Effects of an Injury to the Temporal Lobes

- Difficulty in recognising faces, things or places.
- Difficulty understanding or remembering what people say.
- Difficulty reading.
- Difficulty recognising objects.
- Short-term memory difficulties.
- Changes in sexual behaviour.
- Increased aggression.
The Parietal Lobes
The parietal lobes also tell us where our body is in relation to the objects around us. This allows us to move around without bumping in to things. This function is known as Visuospatial Processing.
The parietal lobes are also important for skills such as maths, spelling, hand-eye coordination and fine motor movements such as tying shoe laces.
Some Effects of an Injury to the Parietal Lobes

- Difficulty naming objects (Anomia).
- Difficulty in distinguishing left from right.
- Difficulties with hand-eye coordination.
- Difficulty making sense of what we see even if we do not have a visual impairment (Visual Perceptual difficulty).
- Difficulty knowing the function of an object.
- Problems with reading (Alexia), writing (Agraphia) or maths (Dyscalculia).
- Difficulty knowing where things are in relation to our own bodies; for example, how close an object is to us (Spatial Awareness Difficulties).
- Reduced self-awareness (Anosognosia).
- Visual Neglect.
The Occipital Lobes
Some effects of an injury to the Occipital lobes:

- Sight defects
- Blurred vision or sight loss.
- Visual hallucinations and distortions.
- Difficulty with identifying colours
- Difficulty recognising words.
- Difficulty recognising when people, or things, are moving .