Get the Booklet
Download the Brain and Brain Injury Publication in pdf format
What are Grey Matter and White Matter?
The brain is made up of two types of tissue – Grey Matter and White Matter. Grey Matter is mainly made of brain cell bodies and dendrites. Its role is to process information. Grey matter is mainly found in the surface layer of the brain.
White Matter lies underneath the grey matter in the brain. White matter is made of the long brain cell fibres that carry messages to, and from, the grey matter. The grey matter and white matter work together to allow us to carry out the things we do on a daily basis.
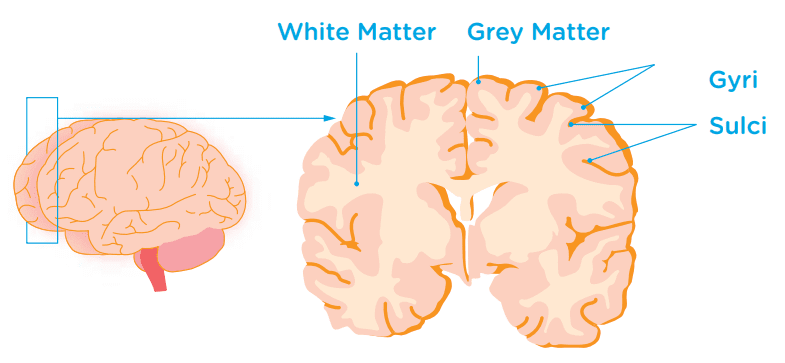
Why does the brain’s surface have wrinkles?
As humans evolved as a species, our brains grew larger to accommodate all the functions that set us apart from other animals. In order to create space for more grey matter, our brains developed many wrinkly folds called Sulci and Gyri. This increased the surface area of the brain and allowed more space for brain cells.
The Brain’s Protection and Support Systems
The brain is a very delicate organ. It is protected and supported by the skull and structures called the meninges and the ventricles.
The Skull
The Skull is a bony structure that protects the brain.
The Meninges
The Meninges are three protective layers that lie between the brain and the skull. They are called the Dura Mater, the Arachnoid and the Pia Mater. The meninges cover and protect the brain.
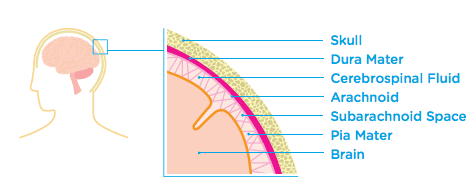
The Ventricles and Cerebrospinal Fluid
- There are four fluid-filled chambers inside the brain called Ventricles.
- The ventricles produce Cerebrospinal Fluid. This is a clear liquid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
- Cerebrospinal fluid protects the brain by cushioning the effect of any blows to the head.
- The cerebrospinal fluid also nourishes the brain.
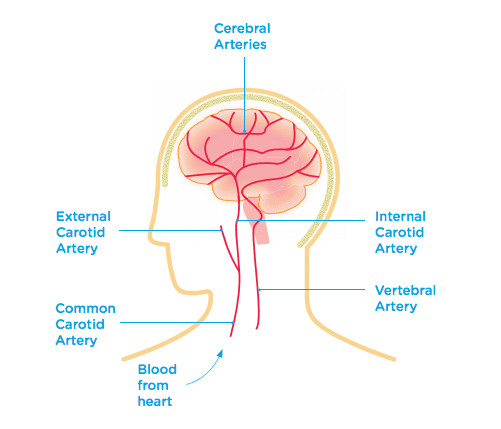
The Brain’s Blood Supply
A good blood supply to the brain is vital. This is because blood carries the oxygen and nutrients that brain cells need to stay alive.
There are a number of important blood vessels supplying the brain, including the Carotid Arteries the Vertebral Arteries and the Cerebral Arteries.
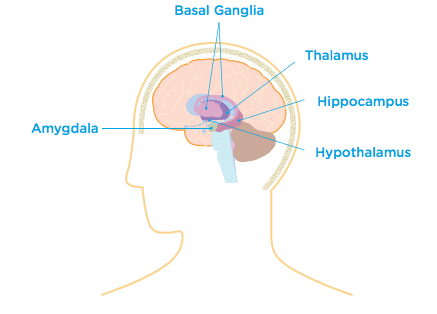
Deep Brain Structures
The Basal Ganglia
The Basal Ganglia are structures that lie deep within the brain, underneath the cerebral cortex. The main role of the basal ganglia is to coordinate movement. They are also important in processing information and in managing our moods.
The Limbic System
The Limbic System is the name given to a collection of structures that lie underneath the temporal lobes. Some of the key structures in the limbic system are the Hypothalamus, the Thalamus, the Hippocampus and the Amygdala. All these structures function by communicating with each other.
The limbic system plays an important role in learning, memory, emotions, instincts, motivation, mood, pleasure, pain and smell. It is also important in managing basic urges; for example, eating when we feel hungry and drinking when thirsty.
The Basal Ganglia
The Basal Ganglia are structures that lie deep within the brain, underneath the cerebral cortex. The main role of the basal ganglia is to coordinate movement. They are also important in processing information and in managing our moods.